270
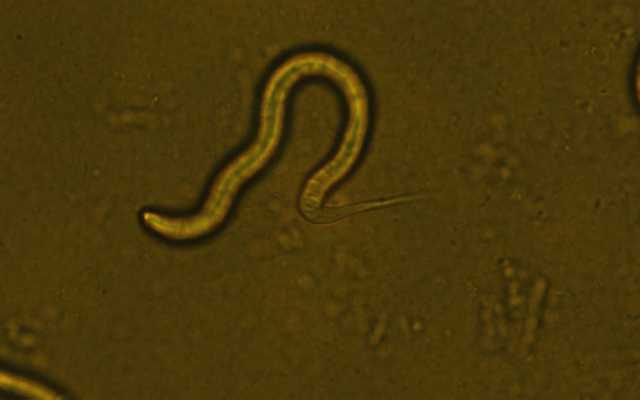
In the course of their work, the researchers placed near the head of worms speakers of different sizes and included sounds with varying volume and frequency, tracking the reaction of worms to the noise. Thus, when exposed to a small speaker, the nematode would curl up and crawl away, but when the speaker size was increased, they showed no response, even though the sound was similar.
The researchers determined that the worms’ cuticle received the most vibrations from the small speaker, and using a tiny microphone, they were able to determine that the sound pressure gradient was greatest when exposed to small sound sources.